- Bitcoin
- Ethereum
- Hemi
- Learn Center
- March 21, 2025
Connecting Bitcoin to DeFi
Bitcoin can and will be an active participant in DeFi. Here’s how.

Bitcoin’s design prioritizes security and decentralization through limited operational complexity. While this has helped it become a store of value, these restrictions create integration challenges with DeFi platforms. The business opportunity lies in developing solutions to unlock Bitcoin’s significant liquidity for DeFi applications, particularly by bridging the gap between Bitcoin and EVM-compatible networks.
How Bitcoin Moves Across Networks
In crypto, one way to move a currency to another chain is to “wrap” it. Typically, a central party takes custody of the assets to be wrapped and issues the wrapped version on the desired blockchain network.
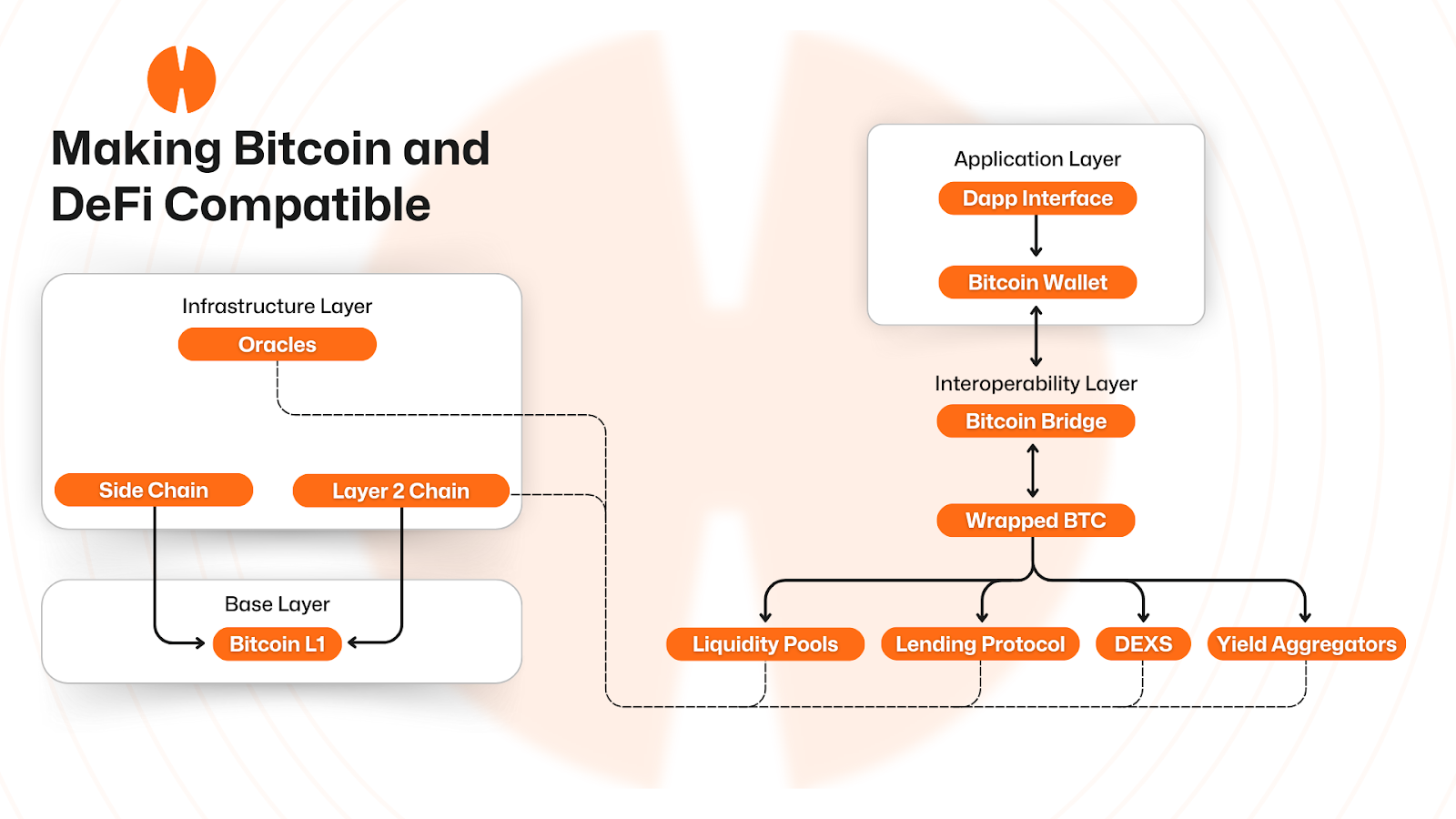
Transporting Bitcoin across chains begins in the application layer, when a user interacts with a client interface, initiating a DeFi protocol of choice with their Bitcoin wallet. The user signs a transaction to initiate the conversion process, and as assets pass through the traditional bridge layer, they are converted to the standardized tokens that all subsequent DeFi interactions utilize.
Here are some examples of these tokens:
Redeemable Tokens – These can be redeemed on a 1:1 basis for the underlying asset, held in a pool by a custodian or protocol. Once the custodian or protocol locks the original asset, a holder of the wrapped asset may burn their wrapped versions to initiate redemption.
Synthetic Wrapped Tokens – A token that is managed via collateralized methods or derivatives. This method relies on oracles and price feeds, as well as over-collateralization to maintain a 1:1 peg.
Non-Redeemable Pegged Tokens – These assets are denominated in one currency but fixed to the value of another via supply and demand mechanics, often supported by collateral and algorithms. Though not directly related to the underlying asset to which they are pegged, they follow its price.
Fractionalized Wrapped Tokens – A token that represents a fraction of ownership of a larger locked asset. Assets are tokenized and divided into smaller pieces, represented by fractional tokens of the original.
Cross-Chain Representations – In this case, a token is locked on one blockchain while the bridge issues a facsimile on the other blockchain, either via a custody model or through a validator-driven protocol.
Whichever method a user opts for, after the conversion process, in the Protocol Layer, the Bitcoin is free to be used across the DeFi ecosystem, trading, forming liquidity pools, lending, or optimizing rewards via a yield aggregator.
An Infrastructure Layer composed of Oracles that feed price data, as well as Layer 2 networks and sidechains that offer execution environments to support the various platforms in the Protocol Layer. In a Base Layer, those execution environments rely on Bitcoin for ultimate settlement
This process suffices to move Bitcoin across chains and has helped to demonstrate the viability of Bitcoin outside the context of holding it onchain as a store of value. However, Hemi has an innovative method that more closely aligns with the decentralized ethos of Bitcoin.
The Hemi Difference
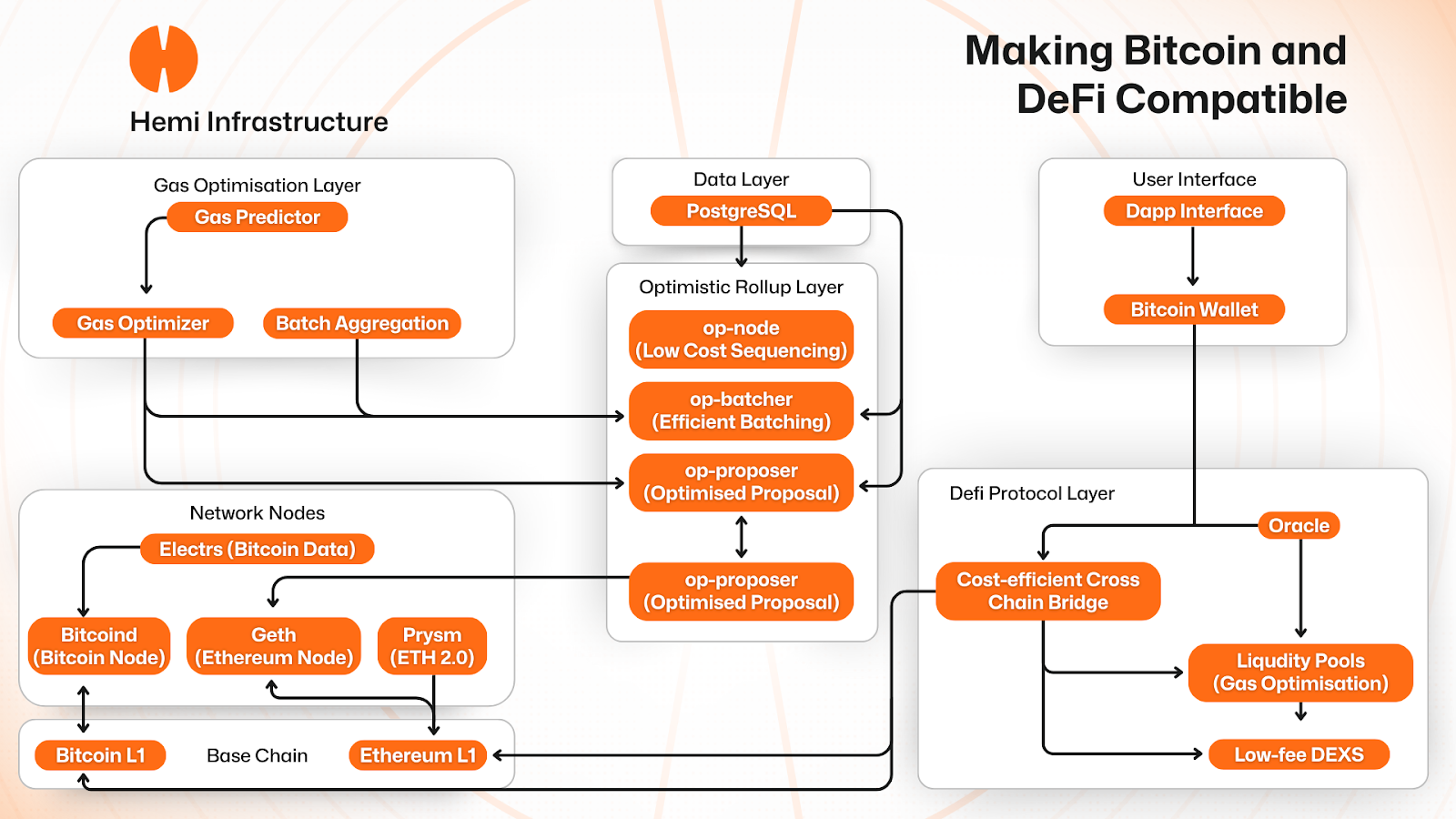
Hemi, on the other hand, has an entirely new method for managing cross-chain traversal. It takes an entirely different – and more secure – approach with its tunnel. By integrating a full Bitcoin node on the hVM, Hemi becomes a connector between Bitcoin and EVM states without requiring a third party to handle custody or external validators. The integration allows Bitcoin to remain natively secure and function with trustless interaction within the hVM DeFi ecosystem. With this approach, Hemi minimizes attack vectors, maintaining decentralized, smart-contract-driven execution.
The dynamic ecosystem of Hemi incorporates a Data Layer in which a PostgreSQL, an open-source relational database, houses data storage accessible to all components. This method delivers efficient cross-component data communication and maintains consistency.
The Network Nodes act as a dual network integration, feature integrations with Bitcoin and Ethereum, creating a seamless connection for both ecosystems. The nodes are interconnected with a scalable Optimistic Rollup Layer responsible for sequencing transactions, efficient transaction batching, proposing blocks, and executing transactions. Keeping pace with all onchain operations within the rollup is a Gas Optimization Layer that uses predictive analysis to ensure low gas fees.
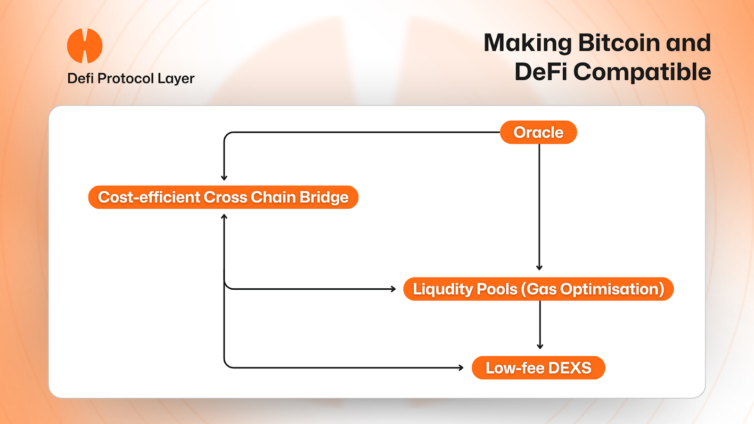
The DeFi Protocol Layer is designed to work seamlessly with Hemi’s infrastructure layers to provide low-cost swaps, efficient cross-chain operations, capital efficiency for liquidity, AI-driven improvements, and a scalable architecture. Liquidity pools reduce gas costs through batched transactions, optimize pricing with AI oracles, and efficiently execute trades. Cross-chain tunnels batch transfers, with help from AI Oracles to achieve precise timing, and leverage the rollup layer for rapid initial finality. A Low-Fee DEX implements features such as AI-powered price discovery, gas-optimized trade execution, and batch processing of trades for fast, low-cost settlement.
With all these components acting as gears in Hemi’s engine, for a user, the experience is simplified allowing them to interact with DeFi protocols with a single interface while cross-chain operations are handled behind the scenes, instead of taking the added step of wrapping Bitcoin through a potentially unstable bridge.
Reduce Risk With Hemi
Of the explored methods that transfer Bitcoin across chains, only Hemi’s dynamic ecosystem featuring tunnels achieves it without compromising decentralization or trustlessness. Traditional wrapping methods – including redeemable tokens, BitGo’s Wrapped BTC (WBTC), or cross-chain representations like Wormhole BTC – rely on intermediaries as custodians or a validator-driven protocol to lock Bitcoin and issue facsimile tokens onto other networks. These methods may have initially enabled limited DeFi interactions for Bitcoin holders but compromise the core principles that make Bitcoin valuable: decentralization, transparency, and security.
For instance, WBTC requires a central custodian, BitGo, to hold and maintain Bitcoin reserves. Users must trust BitGo to maintain the integrity of the reserve and honor redemption requests. Other cross-chain methods that use validators to lock and manage issuance are more decentralized than a custodial protocol but introduce potential vulnerabilities related to the limited size of validator pools and their governance. These vulnerabilities leave openings for exploitation, like the $325 million 2022 Wormhole Bridge attack.
Hemi’s asset tunnels eliminate risks commonly associated with wrapped asset bridges:
Custodial risks – With no centralized entity holding Bitcoin reserves, users no longer rely on the competence, honesty, or dependability of a third party. This helps mitigate the possibility of fraud, regulatory seizure, or reserve mismanagement, issues inherent to cross-chain wrapping approaches.
Transparency – Each transaction and asset lock remains verifiable on-chain, giving users total transparency and the power to perform audits. Where validator-driven bridges may employ off-chain operations that muddle clarity, Hemi’s on-chain operations can be fully analyzed.
Censorship Resistance – Without central control, asset transfers through tunnels to Hemi remain censorship-resistant, aligning with the ethos of accessibility that resonates with Bitcoin’s founding principles.
A Tunnel To Scalability
Hemi’s Tunnel – On Hemi, the Hemi Virtual Machine™ (hVM™) facilitates seamless interaction between Bitcoin and Ethereum states by integrating a full Bitcoin node within an EVM-like environment. As the network maintains protocol-level awareness for both Bitcoin and Ethereum, it enables the movement of assets between chains within this environment. Developers can leverage the Hemi Bitcoin Kit to create Bitcoin-aware, EVM-compatible applications with smart contract interactions that natively comprehend Bitcoin’s state.
By solving for trust-minimized and secure methods to transfer Bitcoin across networks, Hemi’s tunnel provides advantages in scalability and efficiency through reduced intermediary reliance. The streamlined interoperability of hVM transactions allows Bitcoin to participate in Ethereum-based DeFi applications on Hemi, enabling activities like borrowing, lending, and participating in liquidity pools.
By preserving the decentralized approach to cross-chain asset transfers, Hemi maintains Bitcoin’s principles while unlocking its potential to interact with other networks in a seamless, trust-minimized, scalable way. For developers and users seeking to use their Bitcoin and integrate it with broader DeFi applications, Hemi provides a solution aligned with the values of decentralization and cross-chain functionality.